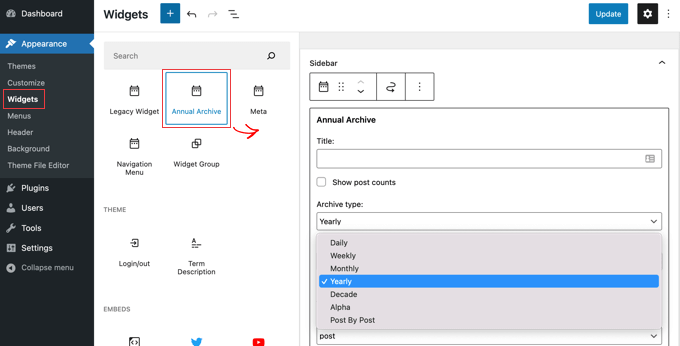
Are you looking for the best WordPress database plugins for your site?
WordPress database plugins can help you clean up your database to improve website performance, assist with website migrations, and more.
In this article, we’ve hand picked some of the best database plugins for your WordPress site.
Why Use a WordPress Database Plugin?
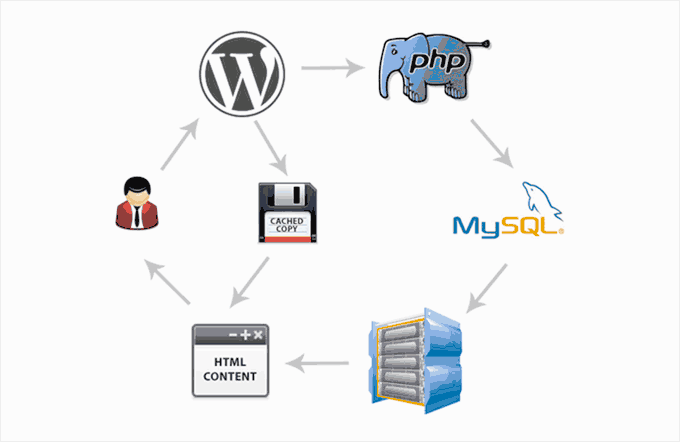
WordPress stores a lot of information in your database, from comments, to posts, user information, plugin data, and more.
Over time your database can become cluttered, which can slow down your website and even cause WordPress errors. WordPress database plugins can help optimize and clean up your database to make sure your site is as fast as possible.
Other WordPress database plugins can help you store and display data, backup your database to keep your site safe, and more.
With that said, let’s show you some of the best WordPress database plugins you can use with your site.
1. UpdraftPlus

UpdraftPlus is the best WordPress backup plugin used by over 3 million websites.
It allows you to create a complete backup of your WordPress website and store it safely in the cloud or your computer. You can choose to backup your entire WordPress site and databases or select specific website files.
You can also backup your site and databases to Dropbox, Amazon S3, FTP, email, Google Drive, and more.
The premium version comes with more addons to migrate and clone websites, use database search and replace, access multisite support, and more.
For more details, see our guide on how to backup and restore your WordPress site with UpdraftPlus.
2. WP-DBManager
WP-DBManager is an all in one tool for WordPress database optimization. The plugin is very feature rich, but it’s still beginner friendly.
It lets you optimize your databases, repair and restore databases, create database backups, and delete database backups you’ve created.
Plus, once you configure the initial settings, it will run in the background, so your WordPress database will always be optimized.
3. WPForms
WPForms is the best contact form plugin for WordPress used by over 5 million websites.
It lets you easily create any kind of form for your WordPress website like contact forms, order forms, user registration forms, and more.
There’s a library of over 300+ templates you can use to get started, and every template can be completely customized with the drag and drop builder.
When a user submits a form on your site, all form data is automatically saved in your WordPress database.
WPForms then takes this data and makes it easy to view within your WordPress dashboard. You can see all the contact data, field labels, number of entries, and more. It’s essentially a frontend database of your contact list.
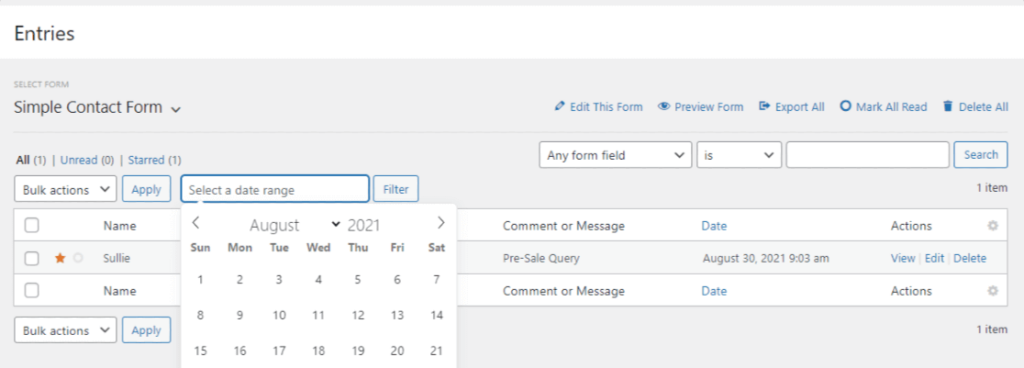
To learn more, see our guide on how to save contact form data in the WordPress database.
You can connect your WordPress forms to Google Sheets or any other email marketing service as well to help improve your workflows and save time.
4. Better Search Replace
Better Search Replace is a useful plugin that can help with moving WordPress to a new domain and various other quick find & replace tasks.
When you’re migrating a website, you usually need to make changes to the database, URLs, media files, and more.
This plugin makes it easy to run a search and replace in your WordPress database. It also has advanced controls, so you can select specific tables, see what fields will be replaced before running the plugin, and more.
It even supports a WordPress multisite network, if you’re migrating an entire network of WordPress sites at once.
5. WP-Sweep

WP-Sweep is a WordPress database plugin that makes it easy to clean up your WordPress database and improve your WordPress performance and speed.
It lets you easily clean up areas like your post metadata, comments, post revisions, uninstalled plugins, and more.
There’s a user friendly settings screen that lets you choose which areas of your database to clean up with a single click.
The plugin also uses the WordPress delete function to remove database data, which helps to ensure there’s no accidental data loss.
6. Formidable Forms
Formidable Forms is a relational database plugin and the most advanced WordPress form builder in the market.
With this plugin, you can upload and collect data through front end forms, then you can display that data on your website in a variety of different ways.
The Formidable Views addon available on the Plus plan lets you display data in a grid, table, calendar, and other formats. This is useful for creating a job board, showing real estate listings, displaying registered users, and more.
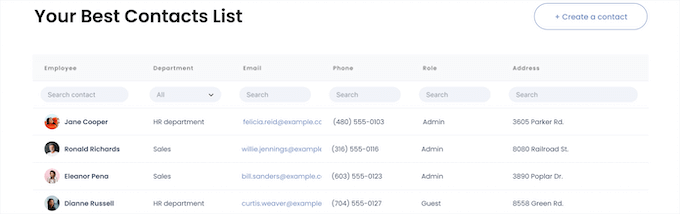
All data submitted through the forms you create with the plugin automatically goes to your WordPress database. Then, you can use the backend interface to sort, filter, and search through your data.
You can also allow users to upload images, blog posts, and other forms of data.
Formidable Forms lets you create a frontend database for WordPress with their advanced Views addon.
7. Easy Username Updater
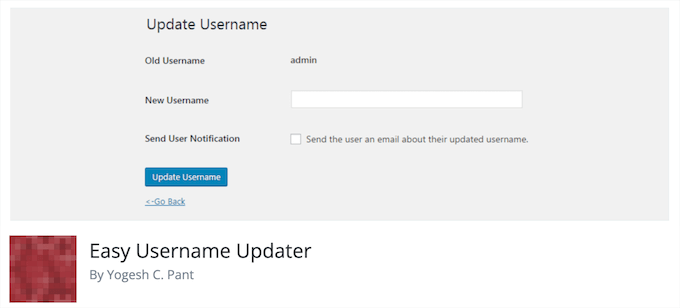
Easy Username Updater is a free plugin that makes it easy to change your WordPress username.
WordPress makes it easy to change your full name from your user profile. But, if you want to change your username, then you’ll need to use a tool like phpMyAdmin to make changes to your database.
This plugin simplifies the process and lets you simply change your username and the usernames of other users right from your WordPress admin panel.
To learn more, see our guide on how to change your WordPress username.
8. JetPack Backup (VaultPress)
JetPack Backup is a popular WordPress backup plugin by Automattic, the company behind WordPress. It was initially launched as VaultPress but has been relaunched and redesigned as Jetpack Backup.
The plugin offers daily automated backups without slowing down your website. These backups also include a full WordPress database backup.
This backup solution is also geared towards WooCommerce store owners, so your order and customer data are always safe.
Beyond backups, you can restore your entire site to a previous version with a single click.
9. TablePress

TablePress is one of the best WordPress table plugins you can use to display your data.
The plugin makes it easy to create beautiful tables without writing any code. There are unique features that make your tables more interactive, like pagination, filtering, sorting, and more.
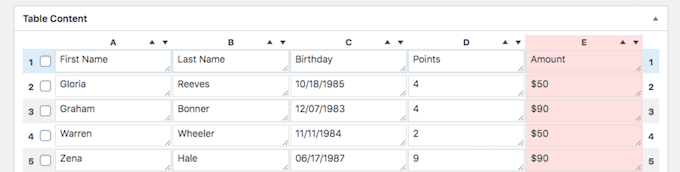
You can import and export existing tables in CSV, Excel, HTML, and JSON format. This makes it easy to migrate your tables from another table plugin.
TablePress stores all of the table data in your WordPress database.
For more details, see our guide on how to add tables in WordPress posts and pages.
10. SearchWP

SearchWP is the best WordPress search plugin and makes it easy to improve WordPress search.
The plugin gives you complete control over your website search algorithm, so you can choose how you want content to rank in your WordPress search results.
It creates its own custom WordPress database to store and maintain its own search index.
This means you get access to your search data, so you can improve your content and create a better user experience.
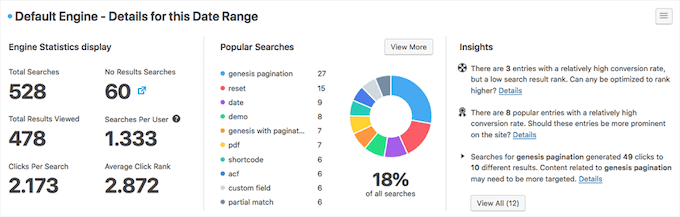
For more details, see our guide on how to use multiple search forms in WordPress.
11. Advanced WordPress Reset

Advanced WordPress Reset lets you reset and restore your WordPress database to it’s original status like a fresh WordPress install.
You can also reset specific areas of your WordPress site such as clean up uploads folder, delete all comments, remove all plugins, etc.
This is a really powerful plugin that’s often used by developers and freelancers when building staging websites or testing. It’s not something you want to use on a live website.
12. wpDataTables

wpDataTables is a premium table plugin that makes it easy to add visually stunning tables to WordPress.
The plugin has an easy to use table builder, so you can create feature rich tables without writing any code.
It’s equipped with features that let you add star ratings, style different cells, add shortcodes, and much more.
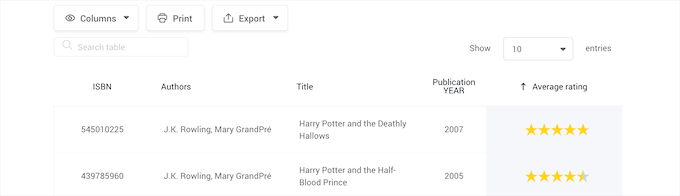
It also has unique features that prevent deleting tables in the WordPress database and can connect your tables to multiple WordPress databases.
Final Thoughts on WordPress Database Plugins
While the above list contains the most popular use-cases of WordPress database plugins, it’s important to emphasize that almost all WordPress plugins interact with the database.
So it’s really impossible to create a best WordPress database plugin list without fully understanding the use-case.
Here are some other bonus WordPress plugins that interact with the database:
- AIOSEO – best WordPress SEO plugin used by over 3 million sites. It stores your website’s SEO data in WordPress database including all 404 errors and other useful insights.
- SeedProd – best drag & drop website builder for WordPress. It lets you create custom WordPress themes without any code, and all data is stored in the database.
- HubSpot – one of the best WordPress CRM software that helps you create a contact database in WordPress. It works well with WPForms.
- MonsterInsights – best WordPress analytics plugin that brings your Google Analytics data inside your WordPress dashboard.
- MemberPress – allows you to create a members only area and sell courses in WordPress. Lets you store a members directory in WordPress database.
- AffiliateWP – best WordPress affiliates plugin that allows you to create and manage a partner referral program in WordPress database and dashboard.
- Sugar Calendar – simple and light-weight event management system allowing you to use your WordPress database as a calendar solution.
- WP Mail SMTP – stores a log of all emails sent by your WordPress site in a database, so you can ensure emails are actually getting delivered to your customers.
That’s just a quick list of bonus plugins that interact with the WordPress database that you may want to use.
We hope this article helped you find the best WordPress database plugins for your site. You may also want to see our guide on how to move WordPress from HTTP to HTTPS and our expert picks of the best business phone services for small businesses.
If you liked this article, then please subscribe to our YouTube Channel for WordPress video tutorials. You can also find us on Twitter and Facebook.
The post 12 Best WordPress Database Plugins – Expert Pick (2022) first appeared on WPBeginner.
March 18, 2022 at 03:03PM